The basic principle of sealing is straightforward – the flexible lip is held against the rotating part (usually the shaft) whilst the casing (or O.D.) is pressed into the housing or bore and holds the seal in place. The sealing lip needs some form of lubrication to avoid overheating and is usually energized by means of a garter spring.
- The 'U' shape of the gasket is not just a design choice; it serves a functional purpose. The three-sided structure enables it to create a tight seal around the circumference of a joining surface, ensuring a secure closure against liquids, gases, or other elements. This design also allows for compression, which enhances the sealing ability when pressure is applied during assembly.
The most common oil seals are the ERIKS types R, RST, M and MST, which correspond respectively to types A, AS, B and BS according to DIN 3760/ISO 6194.
Oil seals are made from multiple compounds and materials. Some of the oldest, still in use today, are leather and felt compounds. The trend in mass production, however, has seen a move towards synthetic rubber or elastomers. Nitrile is by far the most popular material but developments in PTFE have created a surge of interest in buyers needing seals for high-speed shaft rotation applications. Viton is taking over from the polyacrylic and silicone, as it works better in high-temperature applications and has a high-resistance to abrasion and harmful chemicals.
 40mm rubber gasket. Plumbing Systems 40mm rubber gaskets are commonly used in plumbing systems to provide a watertight seal between pipes, fittings, and valves. Their chemical resistance and temperature resistance make them suitable for use in both hot and cold water systems.
40mm rubber gasket. Plumbing Systems 40mm rubber gaskets are commonly used in plumbing systems to provide a watertight seal between pipes, fittings, and valves. Their chemical resistance and temperature resistance make them suitable for use in both hot and cold water systems.Oil seal WG1087811 is used by several automotive manufacturers, such as Opel, Fiat and Suzuki, and serves as a good example for an oil seal where oil leakage can occur if fitted incorrectly.
In this article, we’ve discussed everything you need to know about oil seals, which are sometimes called radial shaft seals. Also, we’ve discussed the various types, their installation, and how to choose the right one for your application. With all these, you will be able to make an informed decision about the best oil seal for your needs.
Oil seals, which are also referred to as radial shaft seals, rotary shaft seals, grease seals, or fluid seals, are used to close the gaps between fixed and moving parts of mechanical equipment. They are put between moving and stationary mechanical parts to make sure that moisture, contaminants, corrosive materials, and abrasives don’t cause any damage to these parts.
Silicone (VMQ) Oil Seals
One of the key benefits of the Spark Plug 794 00082 is its ability to enhance fuel efficiency. By ensuring that the air-fuel mixture is properly ignited, this spark plug helps to maximize the combustion process, leading to improved fuel consumption. This can result in cost savings over time, as you spend less money on gas for your vehicle.
spark plug 794 00082

By far, nitrile is the most popularly used, but buyers who need seals for applications involving high-speed shaft rotation increased interest. Viton is another alternative for silicone and poly-acrylic because it’s more resistant to harmful chemicals and abrasion and works better in higher temperatures.
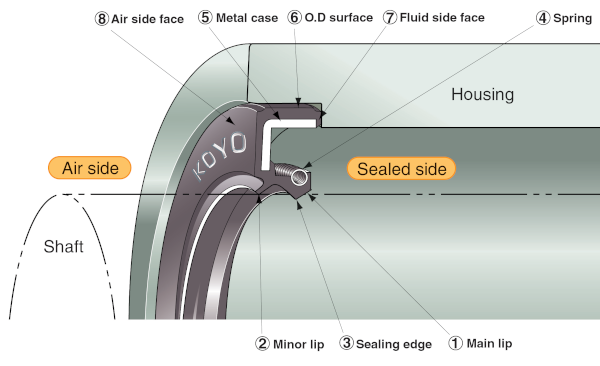
Figure 2: Typically shaped oil seal and component nomenclature
If you are looking for the highest temperature resistant oil seals, Perfluoelastomer can go up to 600°F. If you are more concerned for low temperature, Chloroprene can go all the way down to 40°F, which is why it is used most commonly for refrigeration. And if FDA applications or medical devices are your primary concern, Butyl , the all petroleum compound, will be your best choice. As you can see, when choosing the right material to work with, you must analyze several other key components to help choose the right one.
First, an elastomer, most often nitrile, is vulcanised to a metal ring. This creates a stiffening effect that includes a specialised metal tension spring directly behind the sealing lip, keeping the oil seal firmly in place against the moving part.
 This adaptability translates into better fuel economy, reduced emissions, and increased engine longevity This adaptability translates into better fuel economy, reduced emissions, and increased engine longevity
This adaptability translates into better fuel economy, reduced emissions, and increased engine longevity This adaptability translates into better fuel economy, reduced emissions, and increased engine longevity 794 00055a spark plug.
794 00055a spark plug.3. Seal types and numbering system
Maintenance and Replacement of Gaskets

There are many different materials used to manufacture oil seals.